| 
mUNO Peptide (H-CSPGAK-OH) is a synthetic hexapeptide identified for its high affinity and specificity towards the CD206 receptor, also known as the mannose receptor, predominantly expressed on M2-like tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). This peptide has emerged as a valuable tool in cancer research, particularly in targeting pro-tumoral macrophages within the tumor microenvironment.
Functionality and Biological Importance:
• CD206 Targeting: mUNO binds specifically to the CD206 receptor, facilitating the selective targeting of M2-like TAMs. This interaction is crucial for delivering therapeutic agents directly to these macrophages, which play a significant role in tumor progression and immune evasion.
• Tumor Microenvironment Modulation: By targeting M2-like TAMs, mUNO contributes to reprogramming the tumor microenvironment from a pro-tumoral to an anti-tumoral state, enhancing the efficacy of immunotherapies.
Applications in Research:
• Therapeutic Delivery: mUNO has been utilized to deliver therapeutic agents, such as drugs or nanoparticles, directly to M2-like TAMs, improving the specificity and effectiveness of cancer treatments.
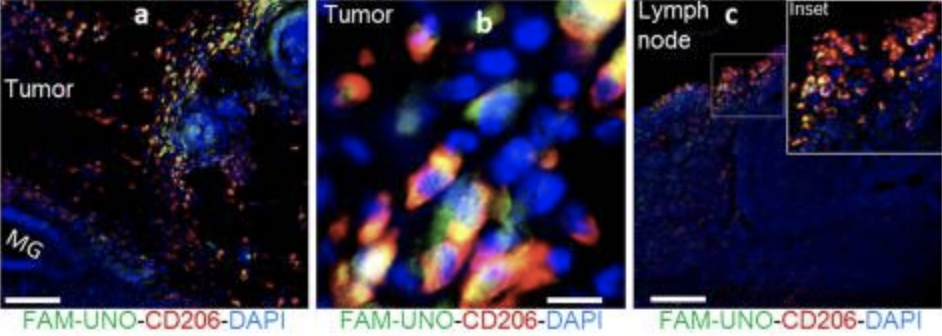
• Diagnostic Imaging: Conjugation of mUNO with imaging agents enables the visualization of M2-like TAM distribution within tumors, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of cancer progression.
• Macrophage Depletion Studies: Researchers have employed mUNO to selectively deplete M2-like TAMs in tumor models, providing insights into their role in cancer biology and therapeutic resistance.
mUNO peptide serves as a potent and specific ligand for CD206, offering significant potential in the targeted modulation of the tumor microenvironment. Its applications in therapeutic delivery, diagnostic imaging, and macrophage depletion make it a valuable asset in cancer research and the development of novel anti-cancer strategies. |
| Scodeller P, Simón-Gracia L, Kopanchuk S, Tobi A, Kilk K, Säälik P, Kurm K, Squadrito ML, Kotamraju VR, Rinken A, De Palma M, Ruoslahti E, Teesalu T. Precision Targeting of Tumor Macrophages with a CD206 Binding Peptide. Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 7;7(1):14655. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14709-x. PMID: 29116108; PMCID: PMC5676682.
Depletion of Mannose Receptor-Positive Tumor-associated Macrophages via a Peptide-targeted Star-shaped Polyglutamate Inhibits Breast Cancer Progression in Mice. Lepland A, Malfanti A, Haljasorg U, Asciutto EK, Pickholz M, Bringas M, Đorđević S, Salumäe L, Peterson P, Teesalu T, Vicent MJ, Scodeller P. Cancer Res Commun. 2022 Jun 28;2(6):533-551
Targeting Pro-Tumoral Macrophages in Early Primary and Metastatic Breast Tumors with the CD206-Binding mUNO Peptide. Lepland A, Asciutto EK, Malfanti A, Simón-Gracia L, Sidorenko V, Vicent MJ, Teesalu T, Scodeller P. Mol Pharm. 2020 Jul 6;17(7):2518-2531
Peptide-guided resiquimod-loaded lignin nanoparticles convert tumor-associated macrophages from M2 to M1 phenotype for enhanced chemotherapy. Figueiredo P, Lepland A, Scodeller P, Fontana F, Torrieri G, Tiboni M, Shahbazi MA, Casettari L, Kostiainen MA, Hirvonen J, Teesalu T, Santos HA. Acta Biomater. 2021 Oct 1;133:231-243
Phage-Display-Derived Peptide Binds to Human CD206 and Modeling Reveals a New Binding Site on the Receptor. Asciutto EK, Kopanchuk S, Lepland A, Simón-Gracia L, Aleman C, Teesalu T, Scodeller P. J Phys Chem B. 2019 Mar 7;123(9):1973-1982 |