|
Description:
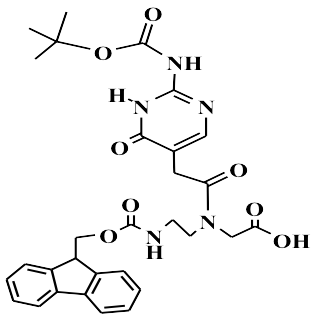
Fmoc-PNA-J(BOC)-OH is a protected peptide-nucleic acid monomer featuring a Boc-protected nucleobase J linked to the standard AEG backbone and capped at the N-terminus by an Fmoc group. It seamlessly integrates into Fmoc/Boc solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) workflows, providing both the acid stability of Boc and the base-labile Fmoc protection for orthogonal deprotection strategies.
Its Boc (tert-butoxycarbonyl) group shields exocyclic amines while allowing swift removal under TFA cleavage. Meanwhile, the Fmoc group safeguards the backbone amine and is efficiently removed with 20–50 % piperidine in DMF.
Key Features:
-
High-Affinity Binding: Typically ≥98–99 %, verified via HPLC
-
Stability & solubility: Soluble in common peptide synthesis solvents like NMP and DMF. Boc and Fmoc protections prevent premature side reactions.
-
Solid Support Compatibility: Ideal for incorporation in automated or manual SPPS peptide‑nucleic acid chimeras, using standard Fmoc/Boc protocols.
-
Optimized Synthesis Protocol: The synthesis involves a repetitive cycle of deblocking, activation/coupling, and capping, typically conducted on a 2umol scale.
PNA synthesis progresses through iterative cycles of Fmoc deprotection and coupling:
- Deprotection: Remove Fmoc using ~20% piperidine in DMF; this releases dibenzofulvene, monitored by UV absorbance.
- Coupling: Activate via HATU (or equivalent) in DMF or NMP; Boc ensures nucleobase selectivity.
- Final cleavage: Following sequence assembly, TFA-based cocktail releases Boc and resin-bound product, yielding full deprotection.
Applications:
- Building block for PNA oligomer synthesis, enabling sequence-specific hybridization applications.
- Supports PNA‑peptide conjugates, thanks to its Fmoc compatibility with peptide chemistries.
- Useful in PNA-based research like FISH probes, diagnostic assays, biosensor platforms, and therapeutic targeting.
|