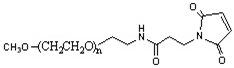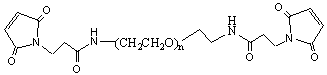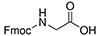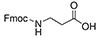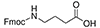Peptide Modifications: Linkers, Spacers and PEGylation

LifeTein provides custom PEGylated conjugates and fatty acid conjugation services for peptides, and small molecules. PEGylation is the process of covalently attaching polyethylene glycol (PEG) polymer chains to peptides. By increasing their molecular mass and shielding them from proteolytic enzymes, PEGylation improves the pharmacokinetics of peptides and proteins. PEGylation reduces renal clearance and results in more sustained absorption after subcutaneous administration, as well as restricted distribution. PEGylations have been shown to significantly improve water solubility, biocompatibility, immunogenicity, and other physico-chemical properties. It is an established method for the delivery of biopharmaceuticals.
The Glutathione (GSH), a tripeptide formed from glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine, is active in many biological redox reactions. The conjugation of glutathione to its PEGylated liposome can be transported through the blood brain barrier in vivo via a sodium-dependent transporter. The GSH PEGylated liposomes enhance delivery of a fluorescent marker in the brain.
LifeTein will PEGylate your peptide, or small molecule, and deliver your PEGylated product with a certificate of analysis, as a regular end-product, for further testing at your site.
As a global partner, we can supply commercial quantities of high quality functionalized PEGs, which are essential for your PEGylated therapeutic proteins.
Our PEGylation services and fatty acid conjugation include:
- Multiple choices: amine reactive PEG acid, carbonyl reactive aminooxy PEG, click chemistry alkyne PEG and PEG azide, DBCO PEG, lipid PEG in drug delivery DSPE PEG, thiol reactive PEG Maleimide, fatty acids of C18, C20 and more
- PEGylation feasibility studies
- Pilot production and process development of PEG-drug conjugate
- Development of PEGylated biosimilars
Discover more about Peptide Drug Conjugation and linkers and spacers.
Pharmacological advantages of peptide PEGylation:
- Improved peptide solubility and enhanced protection from proteolytic degradation. The PEG polymer, along with its associated water molecules, acts like a shield to protect the attached peptide drug from enzyme degradation, thereby limiting adverse immunological effects. PEGylated peptides are more stable over a range of pH and temperature changes compared with their un-PEGylated counterparts.
- Reduced dosing frequency with potentially reduced toxicity. PEG exhibits little toxicity, and is eliminated intact from the body by either the kidneys (for PEGylated drugs <30 kDa) or in the feces (for PEGylated drugs >20 kDa).
- Increased peptide or drug stability and extended circulating life. PEG lacks immunogenicity, and antibodies against PEG in rabbits are generated only if it is combined with highly immunogenic proteins.
LifeTein can attach the PEGs to peptides. Some examples are listed below:
- Monofunctional PEG Maleimide, Molecular Weight of 1K, 2K, 5K, 10K, 20K, or 30K
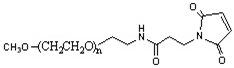
- Bifunctional Maleimide PEG Maleimide, Molecular Weight of 1K, 2K, 5K, 10K, 20K, or 30K
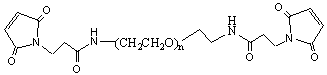
- DSPE-PEG-MAL, Maleimide functionalized PEG Lipid,Molecular Weight of 1K, 2K, or 5K
- Biotin PEG Maleimide, FITC, PEG Maleimide, Multi-arm-4/8 arm-PEG Maleimide
- Fmoc-ε-Ahx-OH, or N-ε-Fmoc-ε-aminocaproic acid; or Fmoc-6-aminohexanoic acid; CAS number: 88574-06-5; Molecular weight: 353.42 g/mol; Molecular Formula: C21H23NO4. Ahx or b-Ala can be used successfully as spacers during the generation of FITC-labeled peptides, which increases the stability of the fluorescent label. FITC can also be linked easily to a cysteine thiol moiety or to the amino group of lysine at any position.Synthesis using an Ahx linker in the lysine core resulted in better yields. Ahx increases the flexibility of peptide chains, which might help keep peptide chains properly solvated during synthesis, thereby preventing aggregation and increasing the amount of viable growing peptide sequences.
Linker/Spacer (Examples)
| Fmoc-Glycine |
2 Carbons |
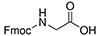 |
3-Amino-3-(2-Nitrophenyl)
Propanoic Acid (ANP Linker) |
3 Carbons |
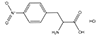 |
| Fmoc-beta-Ala-OH |
3 Carbons |
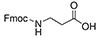 |
4-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
Fmoc-GABA-OH |
4 Carbons |
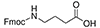 |
| 5-Aminovaleric Acid (Ava) |
5 Carbons |
 |
| Aminohexanoic Acid (Ahx) |
6 Carbons |
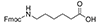
|
mini-PEG or AEEA
Fmoc-NH-PEG2-CH2COOH |
Length of Bonds: 9 |
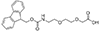
|
mini-PEG2 or AEEP
Fmoc-NH-PEG2-CH2CH2COOH |
Length of Bonds: 10 |
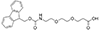
|
AEEEA
Fmoc-NH-PEG3-CH2COOH |
Length of Bonds: 12 |
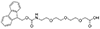
|
AEEEP, or PEG3
Fmoc-NH-PEG3-CH2CH2COOH |
Length of Bonds: 13 |
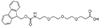
|
AEEEEP, PEG4
Fmoc-NH-PEG4-CH2CH2COOH |
Length of Bonds: 16 |
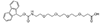
|
AEEEEEP, PEG5
Fmoc-NH-PEG5-CH2CH2COOH |
Length of Bonds: 19 |
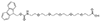 |
1. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (Usually fewer than 6 carbon atoms)
| Name |
Carbon Atoms |
Formula |
Saturation |
| Formic acid |
C1 |
HCOOH |
Saturated |
| Acetic acid |
C2 |
CH₃COOH |
Saturated |
| Propionic acid |
C3 |
CH₃CH₂COOH |
Saturated |
| Butyric acid |
C4 |
CH₃(CH₂)₂COOH |
Saturated |
| Valeric acid |
C5 |
CH₃(CH₂)₃COOH |
Saturated |
2. Medium-Chain Fatty Acids (6 to 12 carbon atoms)
| Name |
Carbon Atoms |
Formula |
Saturation |
| Caproic acid |
C6 |
CH₃(CH₂)₄COOH |
Saturated |
| Caprylic acid |
C8 |
CH₃(CH₂)₆COOH |
Saturated |
| Capric acid |
C10 |
CH₃(CH₂)₈COOH |
Saturated |
| Lauric acid |
C12 |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₀COOH |
Saturated |
3. Long-Chain Fatty Acids (13 to 21 carbon atoms)
| Name |
Carbon Atoms |
Formula |
Saturation |
| Myristic acid |
C14 |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₂COOH |
Saturated |
| Palmitic acid |
C16 |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₄COOH |
Saturated |
| Stearic acid |
C18 |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₆COOH |
Saturated |
| Oleic acid |
C18:1 |
CH₃(CH₂)₇CH=CH(CH₂)₇COOH |
Monounsaturated |
| Linoleic acid |
C18:2 |
CH₃(CH₂)₄(CH=CHCH₂)₂(CH₂)₆COOH |
Polyunsaturated |
| Arachidic acid |
C20 |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₈COOH |
Saturated |
4. Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acids (22 or more carbon atoms)
| Name |
Carbon Atoms |
Formula |
Saturation |
| Behenic acid |
C22 |
CH₃(CH₂)₂₀COOH |
Saturated |
| Lignoceric acid |
C24 |
CH₃(CH₂)₂₂COOH |
Saturated |
| Cerotic acid |
C26 |
CH₃(CH₂)₂₄COOH |
Saturated |
{PEGn}: Fmoc-NH-PEGn-CH2CH2COOH
{mini-PEG}, or {AEEA}, Fmoc-NH-PEG2-CH2COOH, CAS number: 166108-71-0; 2-[2-[2-(Fmoc-amino)ethoxy]ethoxy]acetic acid; Molecular weight: 385.42 g/mol; C21H23NO6
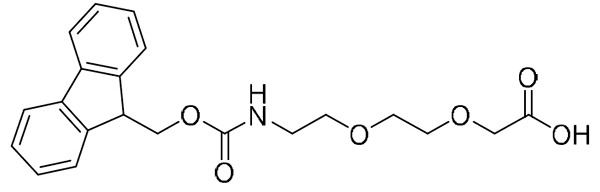
{mini-PEG2}, {AEEP}: Fmoc-NH-PEG2-CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 872679-70-4; Fmoc-NH-PEG2-Propionic Acid; 9-(Fmoc-amino)-4,7-dioxanonanoic acid; Molecular weight: 399.5 g/mol; C22H25NO6
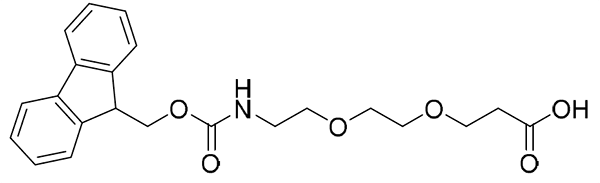
{AEEEA}: Fmoc-NH-PEG3-CH2COOH, CAS number: 139338-72-0; Molecular weight: 429.46 g/mol; C23H27NO7
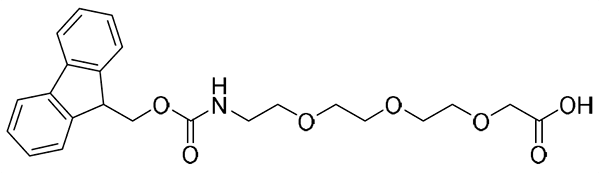
{AEEEP}, or {PEG3}: Fmoc-NH-PEG3-CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 867062-95-1; Molecular weight: 443.50 g/mol; C24H29NO7
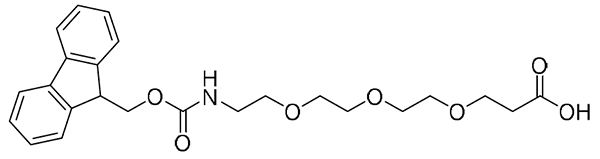
{AEEEEP}, or {PEG4}: Fmoc-NH-PEG4-CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 557756-85-1; Fmoc-NH-PEG4-Propionic Acid, or Fmoc-15-amino-4,7,10,13-tetraoxapentadecacanoic acid; Molecular weight: 487.6 g/mol; C26H33NO8
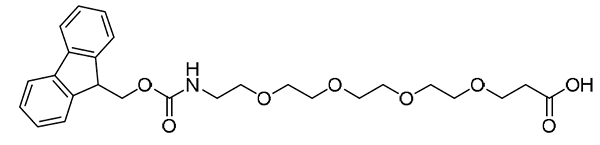
{AEEEEEP}, or {PEG5}: Fmoc-NH-PEG5-CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 882847-32-7; Fmoc-NH-PEG5-Propionic acid, or Fmoc-18-amino-4,7,10,13,16-pentaoxaoctadecanoic acid; Molecular weight: 531.6 g/mol; C28H37NO9
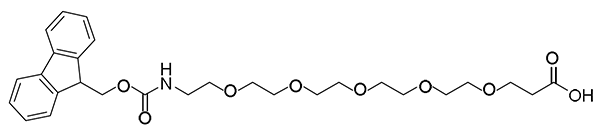
Other PEGs are available.
Fmoc-NH-PEG6 -CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 882847-34-9, Molecular weight: 575.60 g/mol;
Fmoc-NH-PEG7 -CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 1863885-74-8, Molecular weight: 619.58 g/mol;
Fmoc-NH-PEG8-CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 756526-02-0, Molecular weight: 663.58 g/mol;
Fmoc-NH-PEG9-CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 1191064-81-9, Molecular weight: 707.58 g/mol;
Fmoc-NH-PEG10-CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 2101563-45-3, Molecular weight: 751.84 g/mol;
Fmoc-NH-PEG11-CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 2291257-76-4, Molecular weight: 795.84 g/mol;
Fmoc-NH-PEG12-CH2CH2COOH, CAS number: 756526-01-9, Molecular weight: 839.95 g/mol;
Please click here to get a peptide synthesis service quote now!