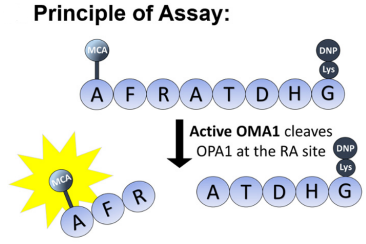
Fluorescence is released when OMA1 recognizes and cleaves the OPA1 8-mer
peptide (fluorescence reporter) presumably at the RA site, from the cited paper
The continual fission and fusion the Mitochondria undergoes to change its shape and function are a key trait of the organelle, one that is regulated by the enzyme OMA1. However, there is little known regarding OMA1 due to the lack of a consistent method to measure its activity. More information is needed to truly gauge the role of OMA1 as a therapeutic agent. This is where one group sought to measure this activity utilizing a fluorescence-based reporter cleavage assay, one where the protease OMA1 activity is measured by MCA fluorescent peptide.
OMA1 activity measured by (MCA-AFRATDHG-(lys)DNP) peptide
The group arrived at this specific sequence as it includes the specific point on protein OPA1 (between the arginine and alanine) that OMA1 cleaves. They would then be able to spectrofluorometrically measure the fluorescent MCA moiety after the cleavage takes place. The assay proved successful in measuring the activity of OMA1, and in an inexpensive manner. The work clearly lays out the foundation for future studies of OMA1, in both its normal and abnormal pathology.
Julia Tobacyk, Nirmala Parajuli, Stephen Shrum, John P. Crow, Lee Ann MacMillan-Crow, The first direct activity assay for the mitochondrial protease OMA1, Mitochondrion, Volume 46, 2019, Pages 1-5, ISSN 1567-7249, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2019.03.001.