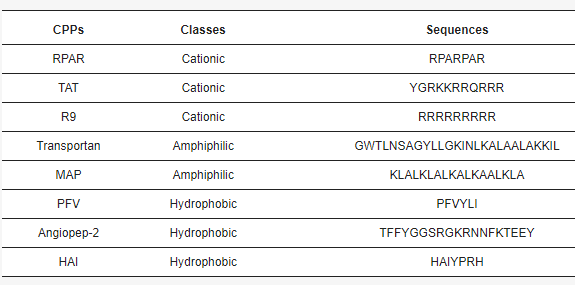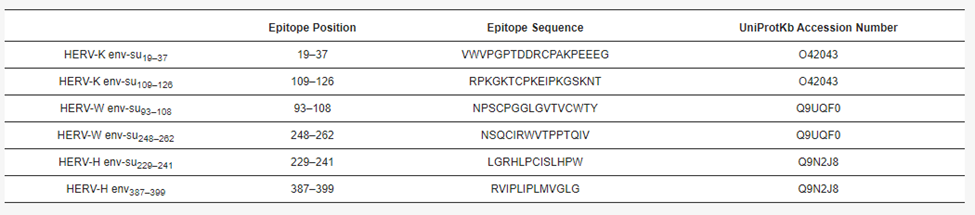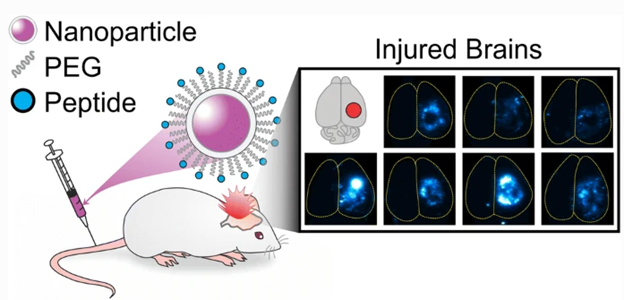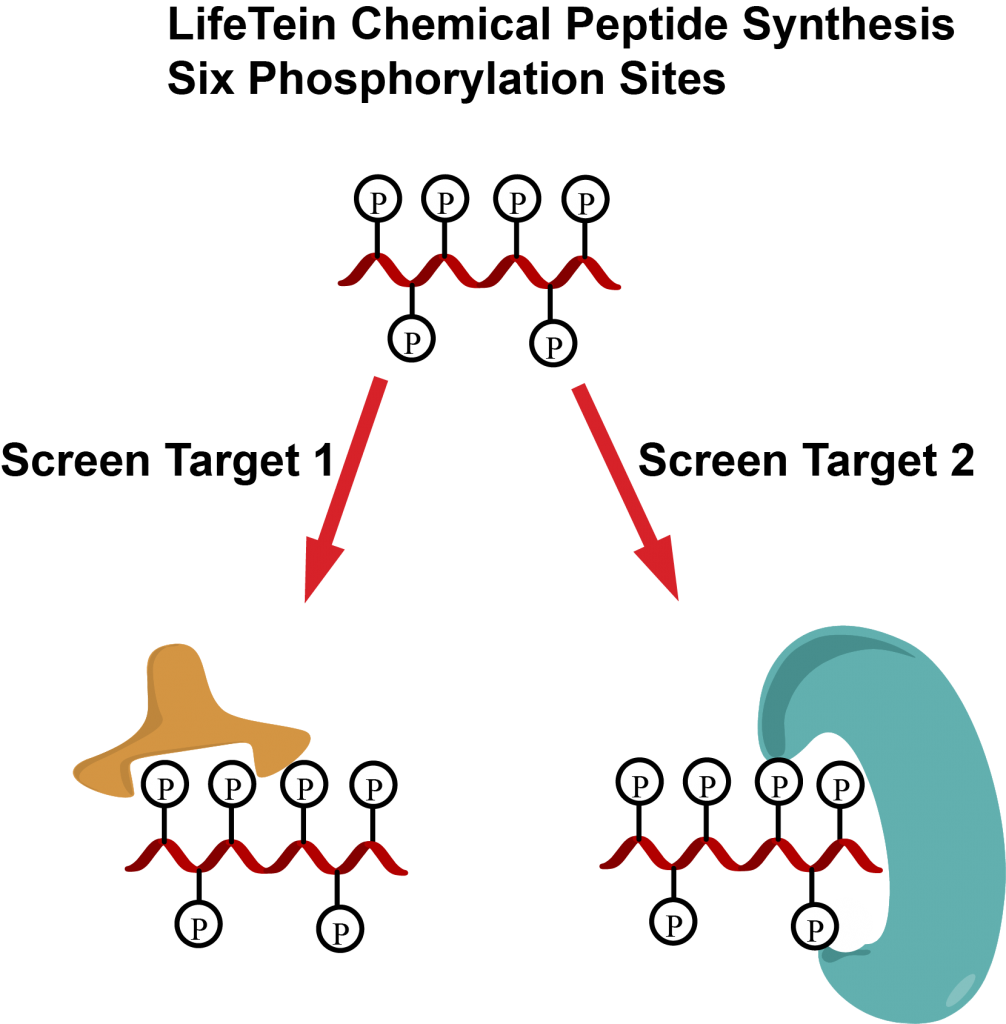
A SARS-CoV-2-specific serological assay is necessary as the global pandemic persists. The ability of such an assay to quantify virus antibodies in high and low COVID-19 incidence communities has a multitude of benefits. These include assessment of exposure rates to the virus, the immune responses to vaccination, and the longevity of antibodies from either infection or vaccination.
Spike Protein Peptide Helps Develop Multiplex Assay
Scientists used multiple resources to develop their SARS-CoV-2 specific serological assay, including a synthetic peptide of the RBD region of the Spike protein (synthetic RBD) by LifeTein. Overall, the assay proved highly sensitive and specific in monitoring the immune response and antibodies in both individuals and communities.
Some innate limitations to this kind of assay would be cross-reactivity with other human coronaviruses, though this was not an issue in the small control group used in Ithaca. The amount of information attainable from the assay will help immensely in the future of this pandemic, as being able to assess infection risks in the population will save countless through precautions.
Guarino C, Larson E, Babasyan S, Rollins A, Joshi LR, Laverack M, et al. (2022) Development of a quantitative COVID-19 multiplex assay and its use for serological surveillance in a low SARS-CoV-2 incidence community. PLoS ONE 17(1): e0262868. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0262868