Fluorescent labeling with Cy5.5 has become a cornerstone in biomedical research, enabling the visualization and tracking of biological molecules in complex environments. This article delves into the specifics of Cy5.5, its applications, and recent advancements in the field.
Key Takeaways:
- Cy5.5 is a near-infrared fluorescent dye used for labeling peptides, proteins, and other biomolecules.
- It offers enhanced sensitivity and specificity for in vivo imaging and diagnostic applications.
- Recent studies have utilized Cy5.5 for targeted drug delivery and imaging of diseases such as endometriosis and testicular disorders.
Introduction to Cy5.5
What is Cy5.5?
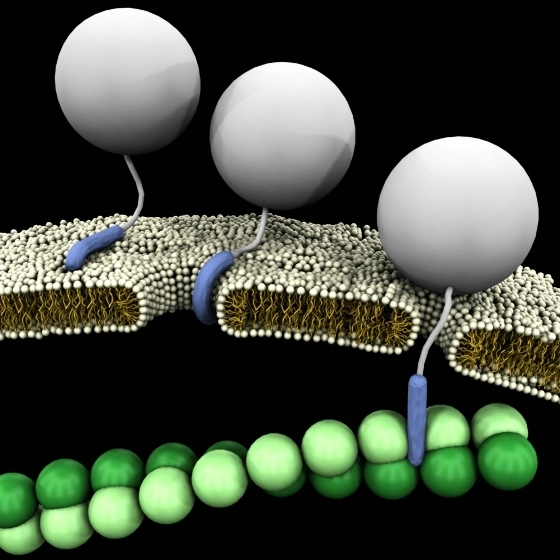
Cy5.5 is a cyanine dye that emits in the near-infrared spectrum, making it ideal for biological imaging due to minimal background fluorescence and deep tissue penetration.
Advantages of Using Cy5.5
- High Sensitivity: Near-infrared fluorescence allows for detection with less interference from biological materials.
- Deep Tissue Imaging: Its emission wavelength enables imaging at greater tissue depths compared to visible light-emitting dyes.
- Versatility: Can be conjugated to a wide range of molecules for various applications.
Applications of Cy5.5 in Research
In Vivo Imaging
Cy5.5 is extensively used in in vivo imaging to study disease processes, monitor therapeutic effects, and track the distribution of biomolecules.
Targeted Drug Delivery
Conjugating Cy5.5 to therapeutic agents allows for the visualization of drug delivery and accumulation in target tissues.
For targeted drug delivery research, explore LifeTein’s peptide synthesis services.
Diagnostic Applications
Cy5.5-labeled probes are used in diagnostic assays and imaging to detect specific biomarkers associated with diseases.
Recent Advances in Cy5.5 Research

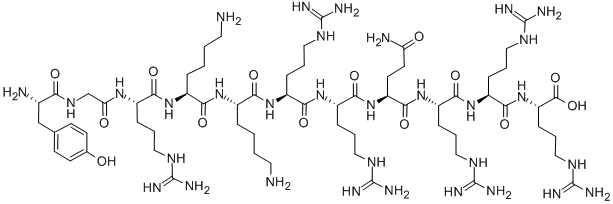
Testicular Targeting with Leydig Cell Homing Peptides
A study identified novel Leydig cell homing peptides for targeted drug delivery to the testis, utilizing Cy5.5 for imaging and validation (read more).
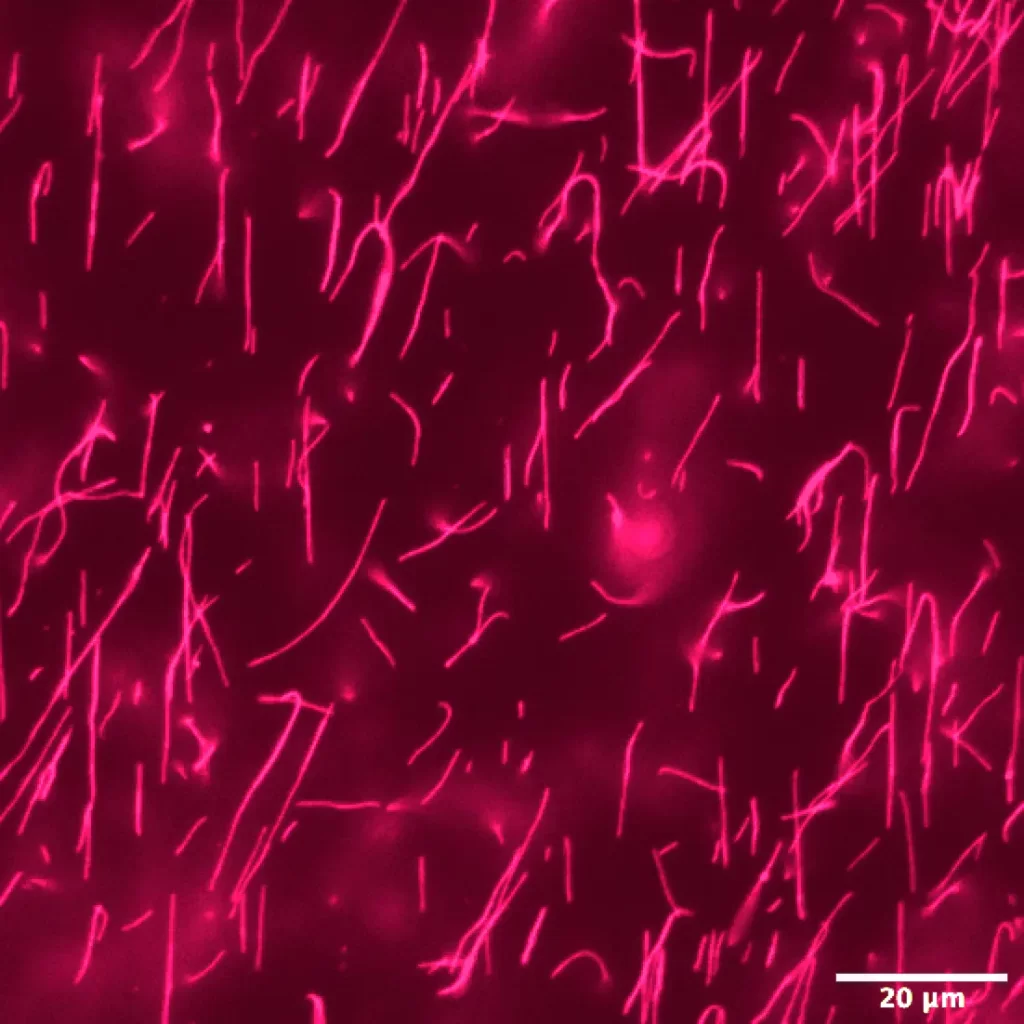
Imaging Endometriotic Lesions
Cy5.5-conjugated nanoparticles were developed to detect endometriotic lesions in a mouse model, demonstrating the potential of Cy5.5 in clinical diagnostics (read more).
Discover more about fluorescent labeling in peptide synthesis at LifeTein’s peptide modifications page.
Challenges and Considerations
Stability and Photobleaching
While Cy5.5 is relatively stable, prolonged exposure to light can lead to photobleaching, affecting quantitative measurements.
Conjugation Efficiency
The efficiency of Cy5.5 conjugation to biomolecules can impact the sensitivity and specificity of imaging applications.
Learn about custom peptide synthesis for research applications at LifeTein’s long peptide synthesis services.
Regulatory and Safety Aspects
The use of Cy5.5, especially in clinical settings, requires careful consideration of regulatory guidelines and safety profiles.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why is Cy5.5 preferred for in vivo imaging?
- Its near-infrared fluorescence minimizes background interference and allows for deeper tissue penetration.
- Can Cy5.5 be used for quantitative analysis?
- Yes, Cy5.5 can be used for quantitative fluorescence measurements, although photobleaching should be considered in long-term studies.
- Are there any limitations to using Cy5.5?
- While highly versatile, Cy5.5’s effectiveness can be limited by photobleaching, conjugation efficiency, and tissue-specific absorption.
Jirwankar, Y., Nair, A., Marathe, S., & Dighe, V. (2024). Phage Display Identified Novel Leydig Cell Homing Peptides for Testicular Targeting. In ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science. American Chemical Society (ACS). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsptsci.3c00330
Talebloo, N., Bernal, M. A. O., Kenyon, E., Mallett, C. L., Mondal, S. K., Fazleabas, A., & Moore, A. (2024). Imaging of Endometriotic Lesions Using cRGD-MN Probe in a Mouse Model of Endometriosis. In Nanomaterials (Vol. 14, Issue 3, p. 319). MDPI AG. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030319